| Question.11 You have an Azure web app named App1. App1 has the deployment slots shown in the following table: 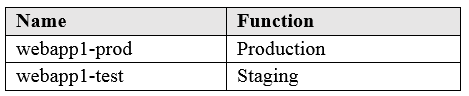 In webapp1-test, you test several changes to App1. You back up App1. You swap webapp1-test for webapp1-prod and discover that App1 is experiencing performance issues. You need to revert to the previous version of App1 as quickly as possible. What should you do? (A) Redeploy App1 (B) Swap the slots (C) Clone App1 (D) Restore the backup of App1 |
11. Click here to View Answer
Answer is (B) Swap the slots
When you swap deployment slots, Azure swaps the Virtual IP addresses of the source and destination slots, thereby swapping the URLs of the slots. We can easily revert the deployment by swapping back.
Deployment slots are live apps with their own host names. App content and configurations elements can be swapped between two deployment slots, including the production slot.
Deploying your application to a non-production slot has the following benefits:
1. You can validate app changes in a staging deployment slot before swapping it with the production slot.
2. Deploying an app to a slot first and swapping it into production makes sure that all instances of the slot are warmed up before being swapped into production.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/deploy-staging-slots
| Question.12 You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1 that contains a resource group named RG1. In RG1, you create an internal load balancer named LB1 and a public load balancer named LB2. You need to ensure that an administrator named Admin1 can manage LB1 and LB2. The solution must follow the principle of least privilege. Which role should you assign to Admin1 for each task? |
12. Click here to View Answer
Answers are both Network Contributor on RG1
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/role-based-access-control/built-in-roles
| Question.13 You have a Microsoft 365 tenant and an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named contoso.com. You plan to grant three users named User1, User2, and User3 access to a temporary Microsoft SharePoint document library named Library1. You need to create groups for the users. The solution must ensure that the groups are deleted automatically after 180 days. Which two groups should you create? (A) A Microsoft 365 group that uses the Assigned membership type (B) A Security group that uses the Assigned membership type (C) A Microsoft 365 group that uses the Dynamic User membership type (D) A Security group that uses the Dynamic User membership type (D) A Security group that uses the Dynamic Device membership type |
13. Click here to View Answer
Answers are (A) & (C): A Microsoft 365 group that uses the Assigned membership type
A Microsoft 365 group that uses the Dynamic User membership type
You can set expiration policy only for Office 365 groups in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
Note: With the increase in usage of Office 365 Groups, administrators and users need a way to clean up unused groups. Expiration policies can help remove inactive groups from the system and make things cleaner.
When a group expires, all of its associated services (the mailbox, Planner, SharePoint site, etc.) are also deleted.
You can set up a rule for dynamic membership on security groups or Office 365 groups.
Incorrect Answers:
B, D, E: You can set expiration policy only for Office 365 groups in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD).
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/office365/admin/create-groups/office-365-groups-expiration-policy?view=o365-worldwide
| Question.14 You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant that contains 5,000 user accounts. You create a new user account named AdminUser1. You need to assign the User administrator administrative role to AdminUser1. What should you do from the user account properties? (A) From the Licenses blade, assign a new license (B) From the Directory role blade, modify the directory role (C) From the Groups blade, invite the user account to a new group (D) None of these |
14. Click here to View Answer
Answer is (B) From the Directory role blade, modify the directory role
Assign a role to a user
1. Sign in to the Azure portal with an account that’s a global admin or privileged role admin for the directory.
2. Select Azure Active Directory, select Users, and then select a specific user from the list.
3. For the selected user, select Directory role, select Add role, and then pick the appropriate admin roles from the Directory roles list, such as Conditional access administrator.
4. Press Select to save.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/fundamentals/active-directory-users-assign-role-azure-portal
| Question.15 You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named contoso.onmicrosoft.com that contains 100 user accounts. You purchase 10 Azure AD Premium P2 licenses for the tenant. You need to ensure that 10 users can use all the Azure AD Premium features. What should you do? (A) From the Licenses blade of Azure AD, assign a license (B) From the Groups blade of each user, invite the users to a group (C) From the Azure AD domain, add an enterprise application (D) From the Directory role blade of each user, modify the directory role |
15. Click here to View Answer
Answer is (A) From the Licenses blade of Azure AD, assign a license
Active Directory-> Manage Section > Choose Licenses -> All Products -> Select Azure Active Directory Premium P2 -> Then assign a user to it.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/fundamentals/license-users-groups
| Question.16 You sign up for Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) Premium. You need to add a user named admin1@contoso.com as an administrator on all the computers that will be joined to the Azure AD domain. What should you configure in Azure AD? (A) Device settings from the Devices blade (B) Providers from the MFA Server blade (C) User settings from the Users blade (D) General settings from the Groups blade |
16. Click here to View Answer
Answer is (A) Device settings from the Devices blade
When you connect a Windows device with Azure AD using an Azure AD join, Azure AD adds the following security principles to the local administrators group on the device:
– The Azure AD global administrator role
– The Azure AD device administrator role
– The user performing the Azure AD join
In the Azure portal, you can manage the device administrator role on the Devices page. To open the Devices page:
1. Sign in to your Azure portal as a global administrator or device administrator.
2. On the left navbar, click Azure Active Directory.
3. In the Manage section, click Devices.
4. On the Devices page, click Device settings.
5. To modify the device administrator role, configure Additional local administrators on Azure AD joined devices.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/devices/assign-local-admin
