| Question.61 HOTSPOT You develop a containerized application. You plan to deploy the application to a new Azure Container instance by using a third-party continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) utility. The deployment must be unattended and include all application assets. The third-party utility must only be able to push and pull images from the registry. The authentication must be managed by Azure Active Directory (Azure AD). The solution must use the principle of least privilege. You need to ensure that the third-party utility can access the registry. Which authentication options should you use? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. Hot Area: 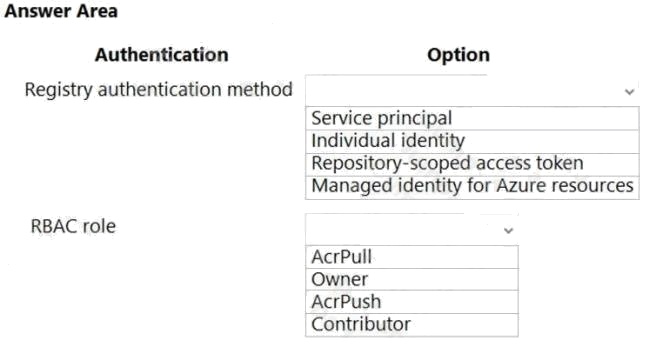 |
61. Click here to View Answer
Answer:
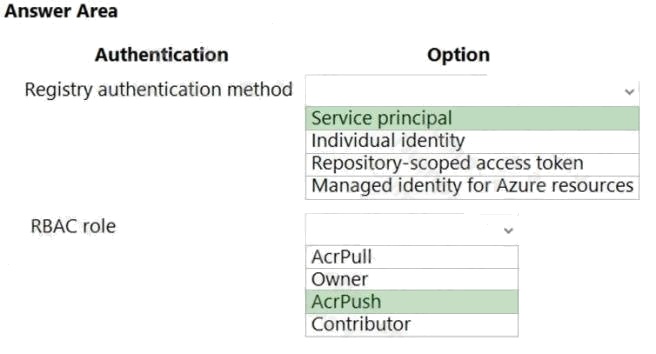
Explanation:
Box 1: Service principal
Applications and container orchestrators can perform unattended, or “headless,” authentication by using an Azure Active
Directory (Azure AD) service principal.
Incorrect Answers:
Individual AD identity does not support unattended push/pull
Repository-scoped access token is not integrated with AD identity
Managed identity for Azure resources is used to authenticate to an Azure container registry from another Azure resource.
Box 2: AcrPush
AcrPush provides pull/push permissions only and meets the principle of least privilege.
Incorrect Answers:
AcrPull only allows pull permissions it does not allow push permissions.
Owner and Contributor allow pull/push permissions but does not meet the principle of least privilege. Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/container-registry/container-registry-authentication?tabs=azure-cli
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/container-registry/container-registry-roles?tabs=azure-cli
| Question.62 HOTSPOT You are developing a web application that makes calls to the Microsoft Graph API. You register the application in the Azure portal and upload a valid X509 certificate. You create an appsettings.json file containing the certificate name, client identifier for the application, and the tenant identifier of the Azure Active Directory (Azure AD). You create a method named ReadCertificate to return the X509 certificate by name. You need to implement code that acquires a token by using the certificate. How should you complete the code segment? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. Hot Area: 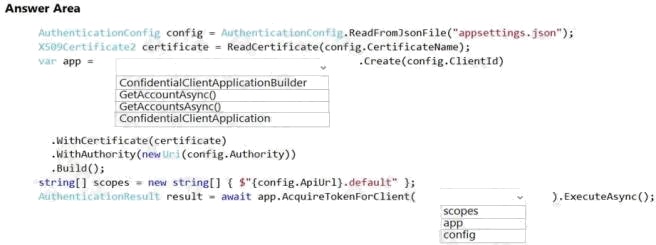 |
62. Click here to View Answer
Answer:
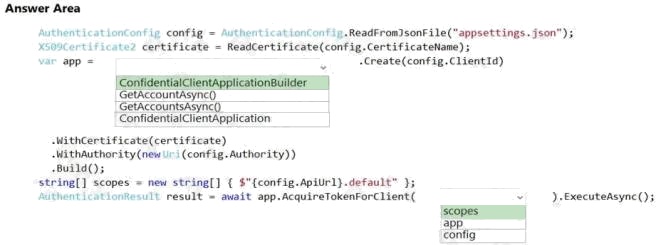
Explanation:
Box 1: ConfidentialClientApplicationBuilder
Here’s the code to instantiate the confidential client application with a client secret: app =
ConfidentialClientApplicationBuilder.Create(config.ClientId)
.WithClientSecret(config.ClientSecret)
.WithAuthority(new Uri(config.Authority)) .Build();
Box 2: scopes
After you’ve constructed a confidential client application, you can acquire a token for the app by calling
AcquireTokenForClient, passing the scope, and optionally forcing a refresh of the token.
Sample code: result = await app.AcquireTokenForClient(scopes) .ExecuteAsync();
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/scenario-daemon-app-configuration
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/develop/scenario-daemon-acquire-token
| Question.63 HOTSPOT You have an Azure Web app that uses Cosmos DB as a data store. You create a CosmosDB container by running the following PowerShell script: $resourceGroupName = “testResourceGroup” $accountName = “testCosmosAccount” $databaseName = “testDatabase” $containerName = “testContainer” $partitionKeyPath = “/EmployeeId” $autoscaleMaxThroughput = 5000 New-AzCosmosDBSqlContainer -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -AccountName $accountName -DatabaseName $databaseName -Name $containerName -PartitionKeyKind Hash -PartitionKeyPath $partitionKeyPath -AutoscaleMaxThroughput $autoscaleMaxThroughput You create the following queries that target the container: SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.EmployeeId > ‘12345’ SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.UserID = ‘12345’ For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. Hot Area:  |
63. Click here to View Answer

Explanation:
Box 1: No
You set the highest, or maximum RU/s Tmax you don’t want the system to exceed. The system automatically scales the
throughput T such that 0.1* Tmax <= T <= Tmax.
In this example we have autoscaleMaxThroughput = 5000, so the minimum throughput for the container is 500 R/Us.
Box 2: No
First query: SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.EmployeeId > ‘12345’
Here’s a query that has a range filter on the partition key and won’t be scoped to a single physical partition. In order to be an
in-partition query, the query must have an equality filter that includes the partition key:
SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.DeviceId > ‘XMS-0001’
Box 3: Yes
Example of In-partition query:
Consider the below query with an equality filter on DeviceId. If we run this query on a container partitioned on DeviceId, this
query will filter to a single physical partition. SELECT * FROM c WHERE c.DeviceId = ‘XMS-0001’
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/how-to-choose-offer https://docs.microsoft.com/en-
us/azure/cosmos-db/how-to-query-container
| Question.64 You are developing a solution that will use a multi-partitioned Azure Cosmos DB database. You plan to use the latest Azure Cosmos DB SDK for development. The solution must meet the following requirements: Send insert and update operations to an Azure Blob storage account.  Process changes to all partitions immediately. Allow parallelization of change processing.   You need to process the Azure Cosmos DB operations. What are two possible ways to achieve this goal? Each correct answer presents a complete solution. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. (A) Create an Azure App Service API and implement the change feed estimator of the SDK. Scale the API by using multiple Azure App Service instances. (B) Create a background job in an Azure Kubernetes Service and implement the change feed feature of the SDK. (C) Create an Azure Function to use a trigger for Azure Cosmos DB. Configure the trigger to connect to the container. (D) Create an Azure Function that uses a FeedIterator object that processes the change feed by using the pull model on the container. Use a FeedRange objext to parallelize the processing of the change feed across multiple functions. |
64. Click here to View Answer
Answer:C
Explanation:
Azure Functions is the simplest option if you are just getting started using the change feed. Due to its simplicity, it is also the
recommended option for most change feed use cases. When you create an Azure Functions trigger for Azure Cosmos DB,
you select the container to connect, and the Azure Function gets triggered whenever there is a change in the container.
Because Azure Functions uses the change feed processor behind the scenes, it automatically parallelizes change
processing across your container’s partitions.
Note: You can work with change feed using the following options:
Using change feed with Azure Functions
Using change feed with change feed processor Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/read-change-feed
| Question.65 HOTSPOT You are developing an application that uses a premium block blob storage account. You are optimizing costs by automating Azure Blob Storage access tiers. You apply the following policy rules to the storage account. You must determine the implications of applying the rules to the data. (Line numbers are included for reference only.)  For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. Hot Area: 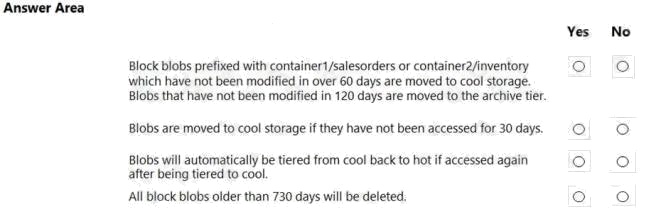 |
65. Click here to View Answer
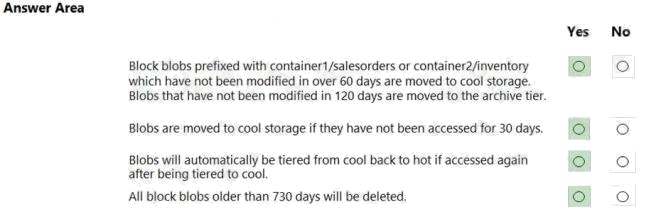
Answer:
Explanation:
Box 1: Yes
Box 2: Yes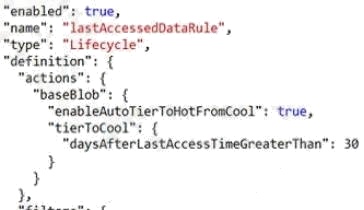
Box 3: Yes
Box 4: Yes
