| Question.76 HOTSPOT You are building a website to access project data related to teams within your organization. The website does not allow anonymous access. Authentication is performed using an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) app named internal. The website has the following authentication requirements: Azure AD users must be able to login to the website.  Personalization of the website must be based on membership in Active Directory groups.  You need to configure the applications manifest to meet the authentication requirements. How should you configure the manifest? To answer, select the appropriate configuration in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. Hot Area:  |
76. Click here to View Answer
Answer:

Explanation:
Box 1: groupMembershipClaims
Scenario: Personalization of the website must be based on membership in Active Directory groups.
Group claims can also be configured in the Optional Claims section of the Application Manifest. Enable group membership
claims by changing the groupMembershipClaim
The valid values are:
“All”
“SecurityGroup”
“DistributionList”
“DirectoryRole”
Box 2: oauth2Permissions
Scenario: Azure AD users must be able to login to the website.
oauth2Permissions specifies the collection of OAuth 2.0 permission scopes that the web API (resource) app exposes to
client apps. These permission scopes may be granted to client apps during consent.
Incorrect Answers: oauth2AllowImplicitFlow. oauth2AllowImplicitFlow specifies whether this web app can request OAuth2.0
implicit flow access tokens. The default is false. This flag is used for browser-based apps, like Javascript single-page apps.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/hybrid/how-to-connect-fed-group-claims
| Question.77 Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution. After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen. You develop Azure solutions. You must grant a virtual machine (VM) access to specific resource groups in Azure Resource Manager. You need to obtain an Azure Resource Manager access token. Solution: Run the Invoke-RestMethod cmdlet to make a request to the local managed identity for Azure resources endpoint. Does the solution meet the goal? (A) Yes (B) No |
77. Click here to View Answer
Answer: A
Explanation:
Get an access token using the VM’s system-assigned managed identity and use it to call Azure Resource Manager You will
need to use PowerShell in this portion.
1. In the portal, navigate to Virtual Machines and go to your Windows virtual machine and in the Overview, click Connect.
2. Enter in your Username and Password for which you added when you created the Windows VM.
3. Now that you have created a Remote Desktop Connection with the virtual machine, open PowerShell in the remote
session.
4. Using the Invoke-WebRequest cmdlet, make a request to the local managed identity for Azure resources endpoint to get
an access token for Azure Resource Manager.
Example:
$response = Invoke-WebRequest -Uri ‘http://169.254.169.254/metadata/identity/oauth2/token?api-version=2018-02-
01&resource=https://management.azure.com/’ -Method GET -Headers @ {Metadata=”true”} Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/managed-identities-azure-resources/tutorial-windows-vm-access-arm
| Question.78 Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution. After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen. You are developing a website that will run as an Azure Web App. Users will authenticate by using their Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) credentials. You plan to assign users one of the following permission levels for the website: admin, normal, and reader. A users Azure AD group membership must be used to determine the permission level. You need to configure authorization. Solution: Configure and use Integrated Windows Authentication in the website.  In the website, query Microsoft Graph API to load the group to which the user is a member.  Does the solution meet the goal? (A) Yes (B) No |
78. Click here to View Answer
Answer: B
Explanation:
Microsoft Graph is a RESTful web API that enables you to access Microsoft Cloud service resources.
Instead in the Azure AD applications manifest, set value of the groupMembershipClaims option to All. In the website, use the
value of the groups claim from the JWT for the user to determine permissions. Reference:
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/waws/2017/03/13/azure-app-service-authentication-aad-groups/
| Question.79 HOTSPOT You are building a website that is used to review restaurants. The website will use an Azure CDN to improve performance and add functionality to requests. You build and deploy a mobile app for Apple iPhones. Whenever a user accesses the website from an iPhone, the user must be redirected to the app store. You need to implement an Azure CDN rule that ensures that iPhone users are redirected to the app store. How should you complete the Azure Resource Manager template? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. Hot Area: 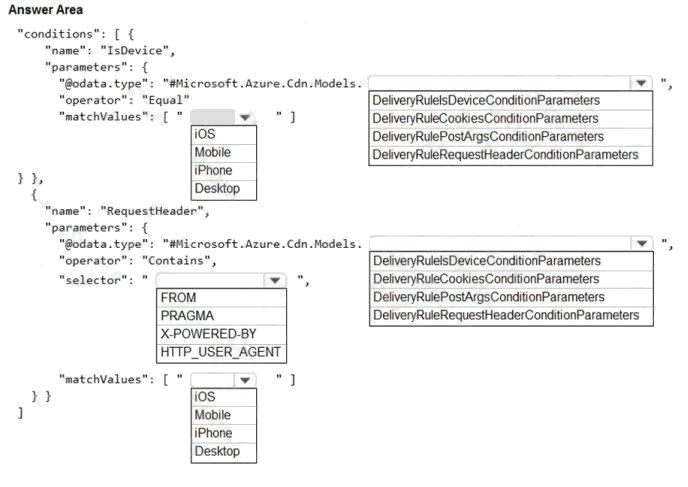 |
79. Click here to View Answer
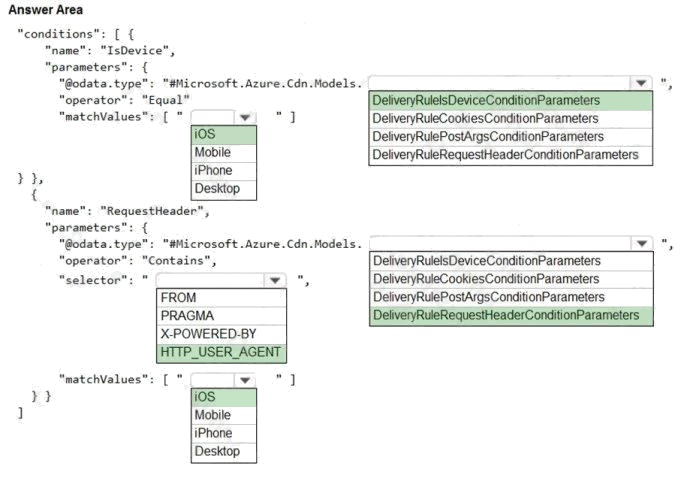
Answer:
Explanation:
Box 1: iOS
Azure AD Conditional Access supports the following device platforms: Android iOS

Windows Phone Windows macOS


Box 2: DeliveryRuleIsDeviceConditionParameters
The DeliveryRuleIsDeviceCondition defines the IsDevice condition for the delivery rule. parameters defines the parameters
for the condition.
Box 3: HTTP_USER_AGENT
Incorrect Answers:
The Pragma HTTP/1.0 general header is an implementation-specific header that may have various effects along the
request-response chain. It is used for backwards compatibility with HTTP/1.0 caches.
“X-Powered-By” is a common non-standard HTTP response header (most headers prefixed with an ‘X-‘ are non-standard).
Box 4: DeliveryRuleRequestHeaderConditionParameters
DeliveryRuleRequestHeaderCondition defines the RequestHeader condition for the delivery rule. parameters defines the
parameters for the condition.
Box 5: iOS
The Require approved client app requirement only supports the iOS and Android for device platform condition.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/conditional-access/concept-conditional-access-conditions
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/conditional-access/concept-conditional-access-grant
| Question.80 Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution. After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen. You develop Azure solutions. You must grant a virtual machine (VM) access to specific resource groups in Azure Resource Manager. You need to obtain an Azure Resource Manager access token. Solution: Use the Reader role-based access control (RBAC) role to authenticate the VM with Azure Resource Manager. Does the solution meet the goal? (A) Yes (B) No |
80. Click here to View Answer
Answer: B
Explanation:
Instead run the Invoke-RestMethod cmdlet to make a request to the local managed identity for Azure resources endpoint.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/active-directory/managed-identities-azure-resources/tutorial-windows-vm-access-arm
