| Question.51 DRAG DROP You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant that contains a security group named Group1. You have an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool named dw1 that contains a schema named schema1. You need to grant Group1 read-only permissions to all the tables and views in schema1. The solution must use the principle of least privilege. Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order. NOTE: More than one order of answer choices is correct. You will receive credit for any of the correct orders you select. Select and Place: 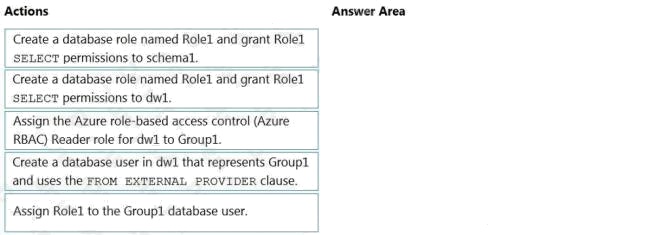 |
51. Click here to View Answer
Answer:
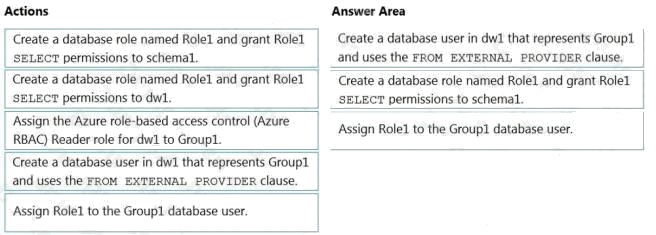
Explanation:
Step 1: Create a database user named dw1 that represents Group1 and use the FROM EXTERNAL PROVIDER clause.
Step 2: Create a database role named Role1 and grant Role1 SELECT permissions to schema1.
Step 3: Assign Role1 to the Group1 database user.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-share/how-to-share-from-sql
| Question.52 You have an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool. You need to ensure that data in the pool is encrypted at rest. The solution must NOT require modifying applications that query the data. What should you do? A. Enable encryption at rest for the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account. B. Enable Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) for the pool. C. Use a customer-managed key to enable double encryption for the Azure Synapse workspace. D. Create an Azure key vault in the Azure subscription grant access to the pool. |
52. Click here to View Answer
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) helps protect against the threat of malicious activity by encrypting and decrypting your
data at rest. When you encrypt your database, associated backups and transaction log files are encrypted without requiring
any changes to your applications. TDE encrypts the storage of an entire database by using a symmetric key called the
database encryption key.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql-data-warehouse/sql-data-warehouse-overview-
manage-security
| Question.53 DRAG DROP You have an Azure data factory. You need to ensure that pipeline-run data is retained for 120 days. The solution must ensure that you can query the data by using the Kusto query language. Which four actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order. NOTE: More than one order of answer choices is correct. You will receive credit for any of the correct orders you select. Select and Place: 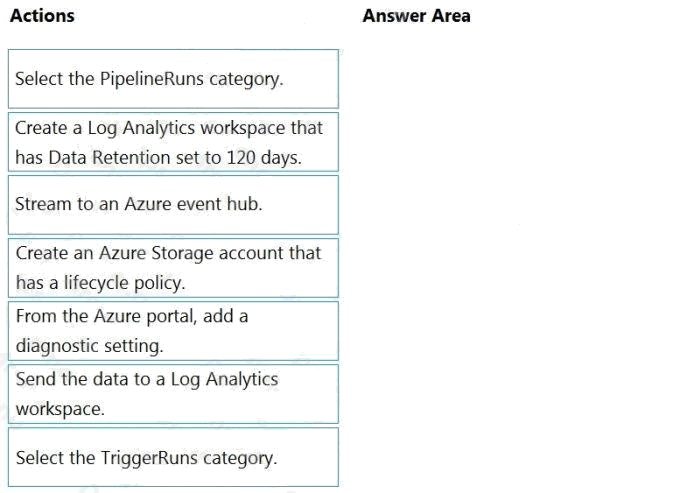 |
53. Click here to View Answer
Answer:
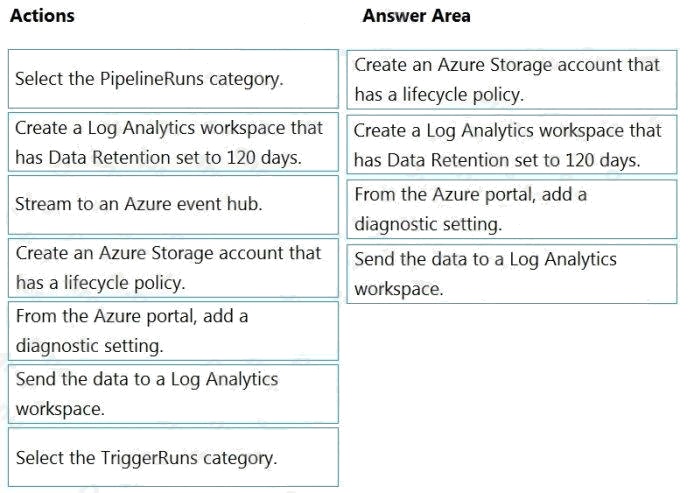
Explanation:
Step 1: Create an Azure Storage account that has a lifecycle policy
To automate common data management tasks, Microsoft created a solution based on Azure Data Factory. The service, Data
Lifecycle Management, makes frequently accessed data available and archives or purges other data according to retention
policies. Teams across the company use the service to reduce storage costs, improve app performance, and comply with
data retention policies.
Step 2: Create a Log Analytics workspace that has Data Retention set to 120 days.
Data Factory stores pipeline-run data for only 45 days. Use Azure Monitor if you want to keep that data for a longer time.
With Monitor, you can route diagnostic logs for analysis to multiple different targets, such as a Storage Account: Save your
diagnostic logs to a storage account for auditing or manual inspection. You can use the diagnostic settings to specify the
retention time in days.
Step 3: From Azure Portal, add a diagnostic setting.
Step 4: Send the data to a log Analytics workspace,
Event Hub: A pipeline that transfers events from services to Azure Data Explorer.
Keeping Azure Data Factory metrics and pipeline-run data.
Configure diagnostic settings and workspace.
Create or add diagnostic settings for your data factory.
1. In the portal, go to Monitor. Select Settings > Diagnostic settings.
2. Select the data factory for which you want to set a diagnostic setting.
3. If no settings exist on the selected data factory, you’re prompted to create a setting. Select Turn on diagnostics.
4. Give your setting a name, select Send to Log Analytics, and then select a workspace from Log Analytics Workspace.
5. Select Save.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/data-factory/monitor-using-azure-monitor
| Question.54 HOTSPOT You have an Azure subscription that is linked to a hybrid Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant. The subscription contains an Azure Synapse Analytics SQL pool named Pool1. You need to recommend an authentication solution for Pool1. The solution must support multi-factor authentication (MFA) and database-level authentication. Which authentication solution or solutions should you include m the recommendation? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. Hot Area: 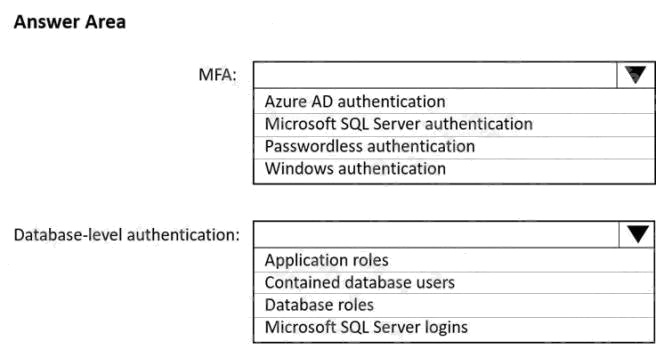 |
54. Click here to View Answer
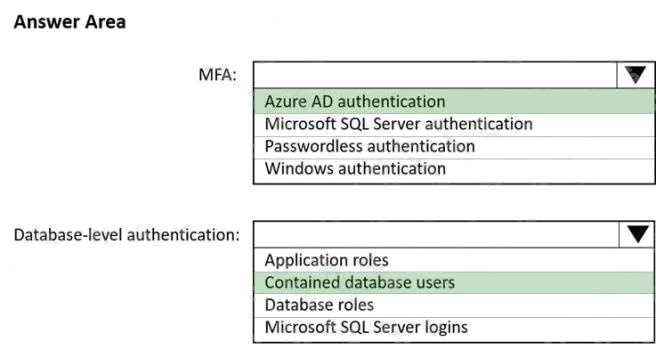
Answer:
Explanation:
Box 1: Azure AD authentication
Azure AD authentication has the option to include MFA.
Box 2: Contained database users
Azure AD authentication uses contained database users to authenticate identities at the database level.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/authentication-mfa-ssms-overview https://docs.microsoft.com/en-
us/azure/azure-sql/database/authentication-aad-overview
| Question.55 HOTSPOT You need to design a data ingestion and storage solution for the Twitter feeds. The solution must meet the customer sentiment analytics requirements. What should you include in the solution? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area. NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point. Hot Area: 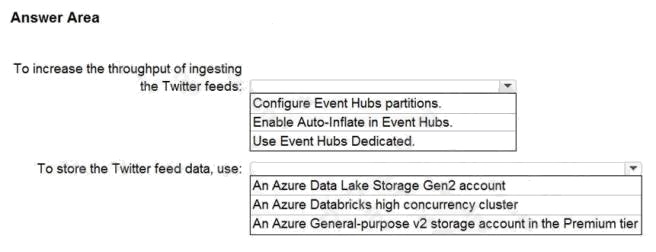 |
55. Click here to View Answer
Answer:

Explanation:
Box 1: Configure Evegent Hubs partitions
Scenario: Maximize the throughput of ingesting Twitter feeds from Event Hubs to Azure Storage without purchasing
additional throughput or capacity units.
Event Hubs is designed to help with processing of large volumes of events. Event Hubs throughput is scaled by using
partitions and throughput-unit allocations.
Incorrect Answers:
Event Hubs Dedicated: Event Hubs clusters offer single-tenant deployments for customers with the most demanding
streaming needs. This single-tenant offering has a guaranteed 99.99% SLA and is available only on our Dedicated pricing
tier.
Auto-Inflate: The Auto-inflate feature of Event Hubs automatically scales up by increasing the number of TUs, to meet
usage needs.
Event Hubs traffic is controlled by TUs (standard tier). Auto-inflate enables you to start small with the minimum required TUs
you choose. The feature then scales automatically to the maximum limit of TUs you need, depending on the increase in your
traffic.
Box 2: An Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account
Scenario: Ensure that the data store supports Azure AD-based access control down to the object level.
Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 implements an access control model that supports both Azure role-based access control
(Azure RBAC) and POSIX-like access control lists (ACLs).
Incorrect Answers:
Azure Databricks: An Azure administrator with the proper permissions can configure Azure Active Directory conditional
access to control where and when users are permitted to sign in to Azure Databricks.
Azure Storage supports using Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) to authorize requests to blob data.
You can scope access to Azure blob resources at the following levels, beginning with the narrowest scope:
– An individual container. At this scope, a role assignment applies to all of the blobs in the container, as well as container
properties and metadata.
– The storage account. At this scope, a role assignment applies to all containers and their blobs.
– The resource group. At this scope, a role assignment applies to all of the containers in all of the storage accounts in the
resource group.
– The subscription. At this scope, a role assignment applies to all of the containers in all of the storage accounts in all of the
resource groups in the subscription. – A management group.
Reference: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/event-hubs/event-hubs-features https://docs.microsoft.com/en-
us/azure/storage/blobs/data-lake-storage-access-control
